Post by Antesky Vicky on Apr 15th, 2025 at 2:32am
With the rapid development of satellite technology, low earth orbit (LEO) satellites have become a disruptive innovation. Located about 100 to 500 miles above the earth’s surface, these satellites have completely changed the way we communicate, collect data and monitor the earth. LEO satellites play a key role in many fields such as telecommunications, earth observation, scientific research and national security. It is expected that by 2029, the size of commercial constellations will increase from 35% to 70%, of which about 65% of the growth will be concentrated in communication applications, involving satellite networks spanning low earth orbit (LEO), medium earth orbit (MEO) and geosynchronous orbit (GEO) satellites.
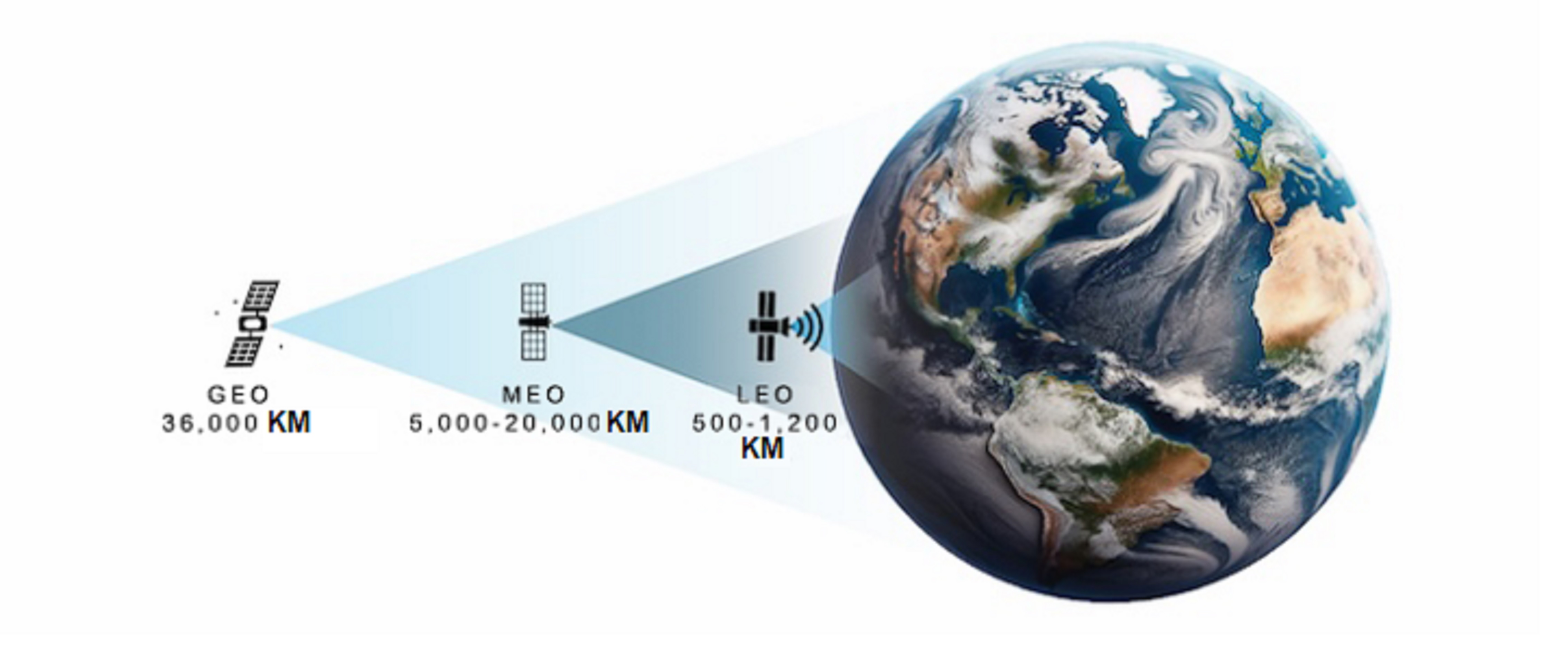
1. Comparison of different satellite orbits
GEO satellites rotate synchronously with the Earth at the same speed, so their position relative to the Earth is fixed, ensuring a fixed pointing angle from any location on the Earth’s surface. On a mobile platform, ground-based GEO directional antennas must continuously point to a designated GEO satellite. These traditional ground-based satellite antennas are large and expensive, have many moving parts, and require regular maintenance.
MEO satellites, such as GPS, are often used for navigation. MEO satellites have their own advantages, but similar to GEO satellites, they are expensive to launch and maintain. Although GEO and MEO satellites each have their uses, they both have issues with latency and data rates.
Satellites play an important role in promoting global connectivity. As shown in Figure 3, they have two main tasks: one is to communicate directly with the earth to provide support for many end-user terminals in different industries; the other is to transmit data back to the earth directly or via inter-satellite links (ISLs). As more LEO satellites are launched, communication speeds are significantly improved and coverage is expanding; the transmission of information from space to the earth becomes more convenient and has less latency.
2. Satellite basic components
Satellites are complex systems that contain multiple functions depending on the mission; this article will focus on the transponder component inside the communications payload module. A transponder is a subsystem in the payload module that is responsible for sending and receiving signals; it usually contains amplifiers, receivers, and transmitters for communication purposes.
3. Integration of satellite and 5G networks
Broadband services provided by large LEO satellite constellations are becoming increasingly popular around the world. This trend, coupled with the integration of satellite networks into the 5G ecosystem, is further driving the growth of the satellite communications market.
In addition, cellular communications are becoming part of the satellite ecosystem. The introduction of 5G wireless technology in 3GPP Release 17 enables 5G systems to serve non-terrestrial networks (NTNs). NTNs are designed to expand global network coverage, especially in rural and remote areas, and facilitate direct connections between mobile devices, the Internet of Things (IoT), and commercial autonomous vehicles and satellites. This integration enables the satellite industry to fully leverage the scale of the 5G ecosystem.
3GPP Release 17 defines 5G New Radio (NR) NTN and 5G IoT NTN, as shown in Figure 4. It focuses on leveraging satellite transparent payload architecture and UEs with GNSS capabilities; Figure 4 shows the expected use cases for 5G NTN.
Other application scenarios include…
Areas with insufficient coverage such as agriculture, mining and forestry
Disaster area communications when terrestrial communication networks are damaged
Broadcasting information over a very wide area
1. Comparison of different satellite orbits
GEO satellites rotate synchronously with the Earth at the same speed, so their position relative to the Earth is fixed, ensuring a fixed pointing angle from any location on the Earth’s surface. On a mobile platform, ground-based GEO directional antennas must continuously point to a designated GEO satellite. These traditional ground-based satellite antennas are large and expensive, have many moving parts, and require regular maintenance.
MEO satellites, such as GPS, are often used for navigation. MEO satellites have their own advantages, but similar to GEO satellites, they are expensive to launch and maintain. Although GEO and MEO satellites each have their uses, they both have issues with latency and data rates.
Satellites play an important role in promoting global connectivity. As shown in Figure 3, they have two main tasks: one is to communicate directly with the earth to provide support for many end-user terminals in different industries; the other is to transmit data back to the earth directly or via inter-satellite links (ISLs). As more LEO satellites are launched, communication speeds are significantly improved and coverage is expanding; the transmission of information from space to the earth becomes more convenient and has less latency.
2. Satellite basic components
Satellites are complex systems that contain multiple functions depending on the mission; this article will focus on the transponder component inside the communications payload module. A transponder is a subsystem in the payload module that is responsible for sending and receiving signals; it usually contains amplifiers, receivers, and transmitters for communication purposes.
3. Integration of satellite and 5G networks
Broadband services provided by large LEO satellite constellations are becoming increasingly popular around the world. This trend, coupled with the integration of satellite networks into the 5G ecosystem, is further driving the growth of the satellite communications market.
In addition, cellular communications are becoming part of the satellite ecosystem. The introduction of 5G wireless technology in 3GPP Release 17 enables 5G systems to serve non-terrestrial networks (NTNs). NTNs are designed to expand global network coverage, especially in rural and remote areas, and facilitate direct connections between mobile devices, the Internet of Things (IoT), and commercial autonomous vehicles and satellites. This integration enables the satellite industry to fully leverage the scale of the 5G ecosystem.
3GPP Release 17 defines 5G New Radio (NR) NTN and 5G IoT NTN, as shown in Figure 4. It focuses on leveraging satellite transparent payload architecture and UEs with GNSS capabilities; Figure 4 shows the expected use cases for 5G NTN.
Other application scenarios include…
Areas with insufficient coverage such as agriculture, mining and forestry
Disaster area communications when terrestrial communication networks are damaged
Broadcasting information over a very wide area