 Copyright © www.antesky.com
Copyright © www.antesky.com1. Effects of sun outage for communication satellites
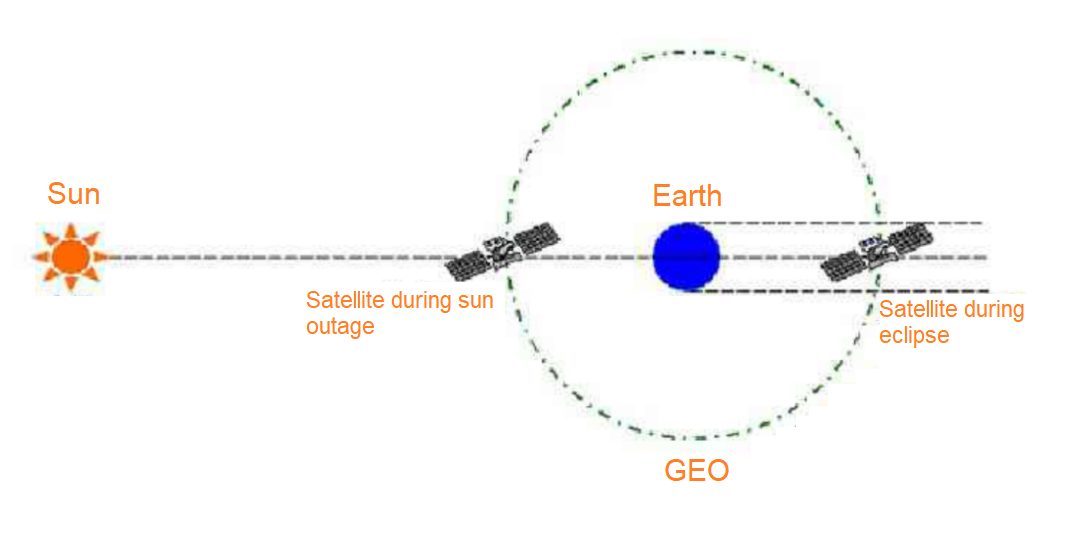
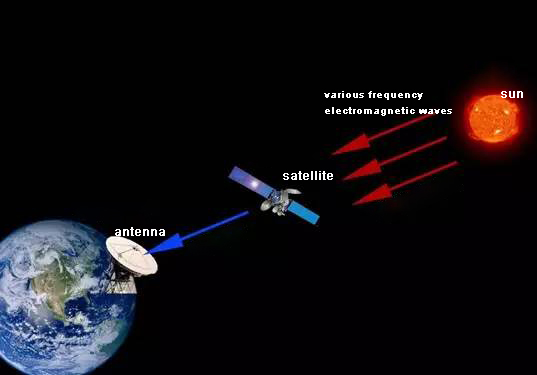
The orbit of the earth rotates with the sun at an inclination angle of 23.5°, so the sun passes over the earth’s equator on March 21 (spring equinox) and September 23 (autumn equinox) each year. Every year around the spring equinox and autumnal equinox, when the sun shines directly on the earth’s equator, the electromagnetic waves emitted by the sun are most intense near the earth’s equator. Since the electromagnetic wave spectrum generated by the sun is very wide, for the earth station, the electromagnetic wave is a huge noise source, causing interference to the satellite signal and seriously deteriorating or even interrupting the receiving line of the satellite. The sun outage diagram is shown below figure 1.
Since communication satellites operate at multiple fixed points over the equator, during this period, if the sun, communication satellites, and ground satellite receiving antennas happen to be in a straight line, the electromagnetic waves at this time will have the strongest impact on artificial satellites, which may cause obstruction of satellite signal transmission. The satellite receiving system on the earth will also receive a large amount of solar radiation clutter while receiving satellite signals. Because useful signals cannot be identified, the signal quality will be degraded or even interrupted. The movement of the moon will also have the same effect on the satellite, but it is much weaker than the sun, so it will not cause the interruption of the satellite signal.
It can be seen that the sun outage is an unavoidable natural phenomenon encountered by the satellite communication system. But the sun outage only affects the downlink of the satellite earth station, not its uplink. It occurs twice a year, namely during the vernal equinox (March 21) and autumnal equinox (September 23), and each time lasts about 6 days. Every time it happens, the satellite earth station will experience the degradation of the received signal quality or the communication interruption in the same period for several consecutive days.
Therefore, in order to ensure the stable operation of the satellite communication system, the date and time of the solar outage should be accurately predicted, so that effective measures can be taken in time to prevent and reduce the interference of the solar outage to the satellite communication system. The solution is to prepare a spare receiving antenna to receive signals from other satellites as a backup when the sun outage occurs.
The date and time of the solar outage are related to the geographic location of the satellite earth station and the electrical characteristics of its receiving satellite antenna.
 Copyright © www.antesky.com
Copyright © www.antesky.com1.1 The relationship between geographical location and sun outage
It can be divided into the effect of longitude and latitude on the duration of the sun outage.
Latitude affects the dates on which solar outage begin and end each year. At the spring equinox, the higher the latitude of the earth station, the earlier the start and end dates of the solar outage; at the autumnal equinox, the higher the latitude, the later the start and end dates of the solar outage. If the longitudes of the two places are the same, then for every 3°difference in latitude, there will be a difference of 1 day between the beginning and end dates of the solar outage in the two places.
Longitude affects when the daily solstice begins and ends. The wester the longitude of the earth station, the earlier the start and end of the daily outage; the easter the longitude, the later the start and end of the daily outage. If the latitudes of the two places are the same, then for every 2° difference in longitude, there will be a difference of about 1 minute between the start and end times of the two places.
1.2 The relationship between earth station electrical performance and solar outage
For an earth station, its sun outage duration begins when the sun enters the 3dB beamwidth of its antenna and ends when it leaves its 3dB beamwidth. Therefore, the duration of the sun outage of the earth station is related to its receiving frequency and the size of the antenna diameter.
The higher the receiving frequency and the narrower the 3dB beamwidth of the antenna, the shorter the duration of the solar outage. The larger the antenna aperture and the narrower the 3dB beamwidth, the shorter the duration of the solar outage.
2. Effects of satellite eclipse for communication satellites
Satellite eclipse, refers to the phenomenon that the artificial satellite is blocked by the surrounding celestial bodies and cannot receive sunlight. There are two types of eclipses: terrestrial eclipses and lunar eclipses. Like solar eclipse and lunar eclipse, when the earth moves between the sun and the communication satellite, the satellite is in the shadow of the earth, which is the terrestrial eclipse; and when the moon moves between the sun and the communication satellite, the same situation will occur, which is a lunar eclipse. The diagram of eclipse is shown below figure 2.
Because the communication satellites use solar power, the solar cells cannot get sunlight and cannot work normally when a satellite eclipse occurs. The on-board battery can only maintain the rotation of the satellite and cannot support the normal operation of the transponder. Therefore, measures should be taken to reduce the energy consumption on the satellite when a satellite eclipse occurs. Generally, some measures are taken to reduce power consumption by shutting down some equipment on the satellite.
For communication satellites in GEO orbits, eclipses usually occur around the spring and autumnal equinoxes, and each time they occur continuously for 45 days, a total of 90 days, and the 2 days of spring and autumnal equinoxes have the longest eclipse duration of 72 minutes. The capacity of the current satellite battery has been greatly improved. During the period of satellite eclipse, the satellite can be guaranteed to work normally. Therefore, the problem of satellite eclipse can be ignored, but the phenomenon of satellite eclipse still exists.
In order to make the satellite eclipse occur in the time when the communication service in the service area is the lowest, the sub-satellite point (that is, the intersection point between the satellite and the center of the earth and the earth’s surface) should be moved eastward or westward to adjust the time when the satellite eclipse occurs to ensure the normal operation of the satellite. However, the offset will change the elevation angle of the earth station to point the satellite, which will bring adverse effects, increase the transmission loss, and weaken the receiving field strength. If the receiving antenna has a small aperture and poor antenna accuracy, it will cause the phenomenon of signal pause and discontinuity. In order to prevent the influence of satellite eclipse, it is necessary to increase the aperture of the receiving antenna and calibrate the precision of the antenna so that the receiving field strength of the antenna is at the strongest value.