Power amplifier (PA) or up-converter power amplifier BUC (Block Up-Converter) is a device used in wireless communication, radar, and satellite communication.
Its main function is to effectively convert weak signals into strong output signals by increasing the power of the signal so that it can be effectively transmitted through the antenna.
The L-band signal output by the satellite modem can be converted into a high-frequency RF signal and transmitted back to the C-band, Ku-band or Ka-band satellite.
The performance of microwave power amplifiers/BUC(Block Up Converter) directly affects the transmission distance, signal quality and overall efficiency of wireless communication systems. With the rapid development of science and technology, microwave power amplifiers/BUC(Block Up Converter) have evolved
The evolution process from low efficiency to high efficiency is constantly driving the progress and innovation of related technologies.
1.Early Development of Microwave power amplifiers/BUC(Block Up Converter)/BUC (Block Up-Converter)
With the rapid development of semiconductor technology, solid-state microwave power amplifiers/BUC(Block Up Converter) have gradually emerged. Solid-state amplifiers have the advantages of small size, light weight, high reliability, and low power consumption, and have gradually replaced the dominant position of vacuum tube amplifiers in the microwave field. Solid-state microwave power amplifiers/BUC(Block Up Converter) mainly include traveling wave tube amplifiers (TWTA) and solid-state power amplifiers/BUC(Block Up Converter) (SSPA). Today we will introduce several major power amplifiers/BUC(Block Up Converter) includingHPA, TWTA, TWTB, SSPA, SSPB, Klystron, and BUC
2.1 HPA (High-Power Amplifier):
Function:A general term for any amplifier that boosts the power of a signal to a high level for satellite transmission.
Types:It encompasses various technologies like TWTA, SSPA, and Klystron
Use Cases:Used in applications that require high-power output to send signals to satellites, overcoming path loss in the communication channel.
2.2 TWTA (Traveling Wave Tube Amplifier):

Function:A type of HPA that amplifies microwave signals using a traveling wave tube (TWT). It’s commonly used in satellite communication due to its ability to handle high power and broad bandwidth.
Advantages:High efficiency, high power output, wide bandwidth, suitable for high-frequency (microwave) applications.
Disadvantages:Larger in size, requires more power, and generates more heat, requiring cooling.
Use Cases:Broadcast satellites, deep space communication, and high-power communication links.
2.3 TWTB (Traveling Wave Tube Block):
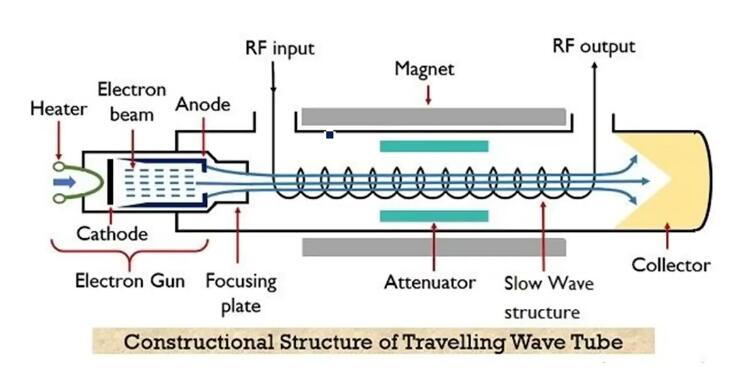
Function:A component or subassembly within the TWTA system that contains the traveling wave tube and associated parts.
Purpose:Focused on providing the core amplification within the TWTA unit.
Use Cases:Used as part of a TWTA system for high-power amplification of signals in satellite communication.
2.4 SSPA (Solid-State Power Amplifier):
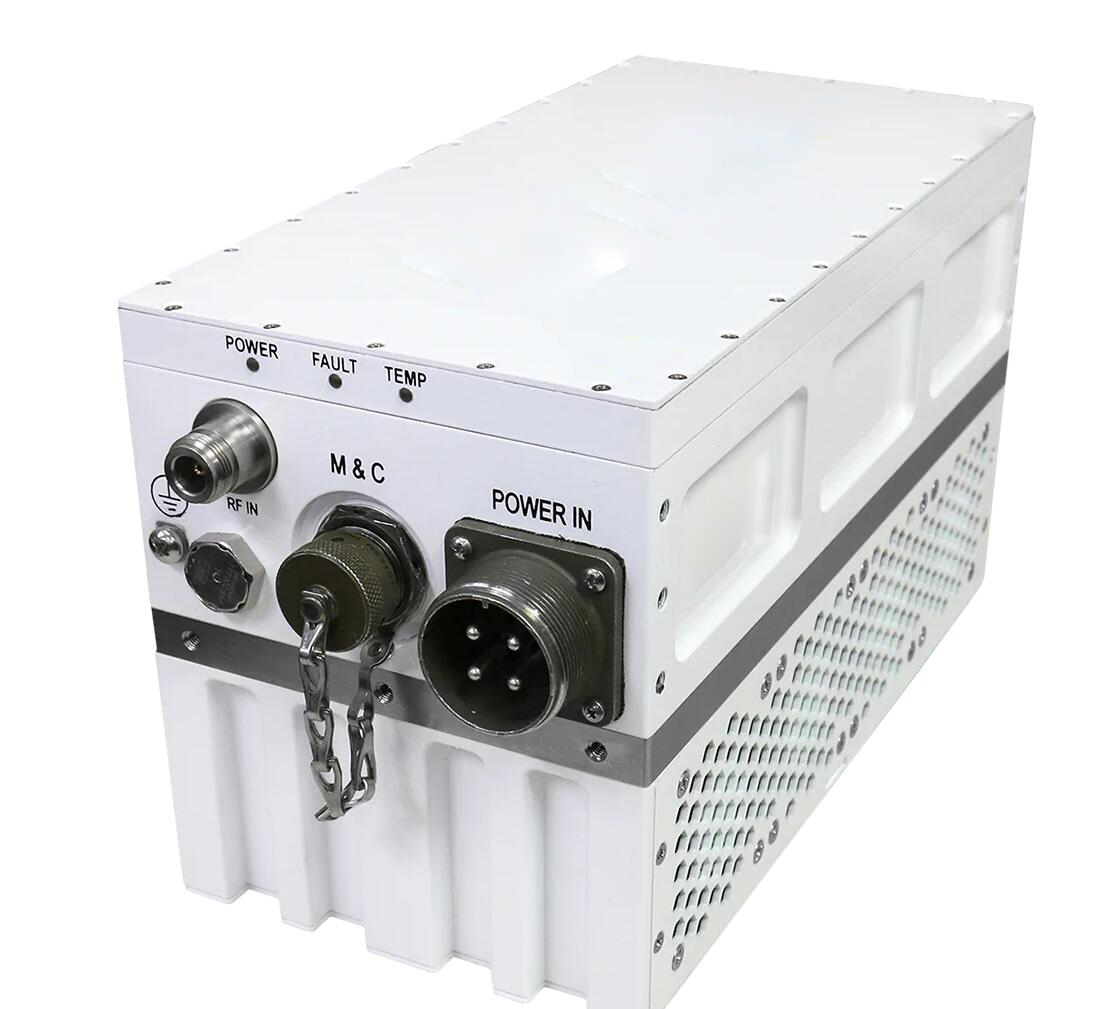

Function:An amplifier that uses solid-state devices (e.g., transistors) to boost signal power. It’s an alternative to TWTA, offering advantages in size, reliability, and power efficiency.
Advantages:Compact, lighter, more reliable, requires less maintenance, more energy-efficient, and has better power efficiency compared to TWTAs.
Disadvantages:Typically lower power output and narrower bandwidth than TWTA, though these limitations are improving with newer technology.
Use Cases:Often used in VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminals), low to medium power satellite uplinks, and applications where size and weight are critical factors.
2.5 SSPB (Solid-State Power Block):

Function:A subassembly or module that contains the solid-state amplification components, similar to TWTB but for solid-state systems.
Purpose:Provides the solid-state amplification within an SSPA unit.
Use Cases:Used in smaller satellite communication systems where reliability and efficiency are prioritized over sheer power output.
2.6 Klystron:
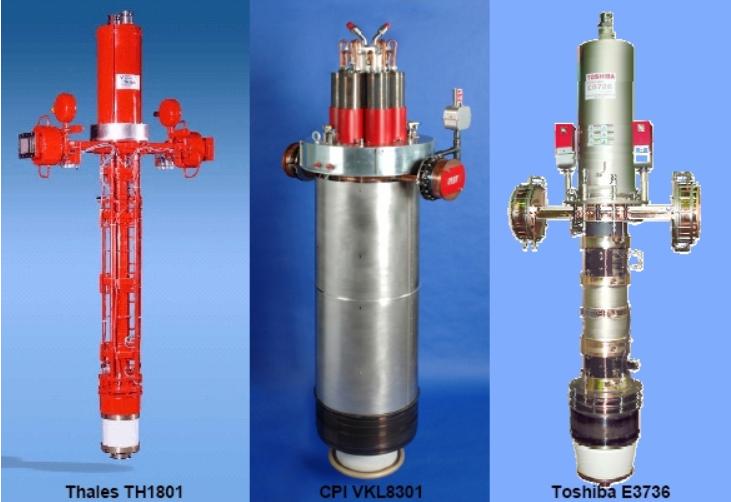

Function:A type of vacuum tube amplifier, similar to a traveling wave tube but based on a different operating principle. Klystrons amplify microwave signals by modulating an electron beam.
Advantages:Extremely high power output, excellent for very high-frequency and high-power applications (e.g., radar, broadcast transmitters).
Disadvantages:Large, heavy, expensive, requires high voltage, and has more complex cooling requirements compared to SSPAs.
Use Cases:Used in ground-based radar, broadcast transmitters, and some satellite communication systems where very high power is needed.
2.7 BUC (Block Upconverter):
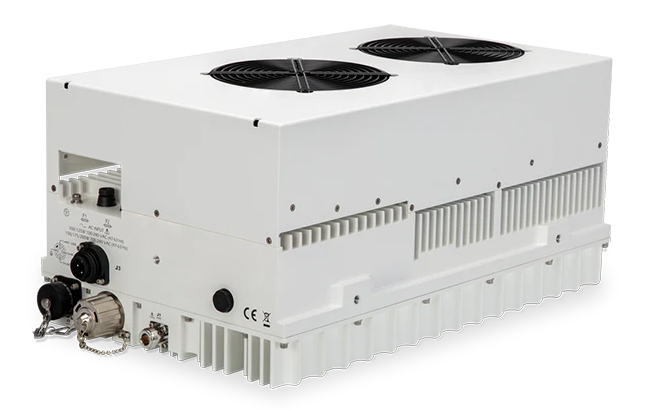

Function:A device that converts a lower Intermediate Frequency (IF) signal to a higher Radio Frequency (RF) signal for transmission. The BUC typically includes an amplifier to ensure the signal is strong enough for satellite transmission.
Amplifier Type:The amplifier in a BUC can be either a TWTA, SSPA, or Klystron, depending on the power and frequency requirements.
Use Cases:Essential in satellite uplink systems, converting an IF signal (like L-band or 70 MHz) to a high-frequency RF signal (e.g., C-band, Ku-band, or Ka-band) for communication with satellites.