Satellite Internet Forum.
Welcome, Guest. Forum rules.To search this site click here > SATSIG search
| Home Login Register |
| › Recent Posts |
| 1 | Anything else / General and other topics / Re: Satellite orbit height, speed and period calculator on: Yesterday at 6:34pm |
||
|
|
|||
Has anyone recently tried my orbit calculator ? Please tell me how you get on and if any problems or errors detected. Thanks. Eric. |
|||
| 2 | Anything else / General and other topics / Re: Challenges, opportunities, and innovations in the space tech industry "Defying Gravity" on: Feb 26th, 2026 at 1:43pm |
||
|
|
|||
Here is a new article you might like to read. It discusses possible problems with LEO orbit satellites and explains the advantages of stratospheric platforms as an alternative. Stratospheric platforms operate within the atmosphere at say 20km altitude. Existing LEO operations are described as critically important to civilisation but as being vulnerable to a number of serious risks. Read more here: https://svrgn.substack.com/p/when-leo-fails-the-case-for-stratospheric Title: "When LEO Fails: The case for stratospheric infrastructure" I think it nicely encompasses all of "Challenges, opportunities, and innovations" You need to learn a new acronym "HAPS" = High Altitude Platform Station See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High-altitude_platform_station Eric |
|||
| 3 | VSAT technology and installation / Dish pointing and alignment / 1.2m Manual Flyaway Antenna Station – Reliable Satellite Communication Wherever You Go on: Feb 26th, 2026 at 7:30am |
||
|
|
|||
In today’s fast-moving communication environment, reliable satellite connectivity is essential for operations in remote, temporary, or infrastructure-limited locations. The 1.2m Manual Flyaway Antenna Station is designed to deliver stable, high-performance satellite communication with the flexibility of rapid field deployment. It provides an ideal balance between mobility, durability, and signal performance, making it a preferred choice for professional users worldwide. 1. Designed for Rapid Deployment The 1.2m manual flyaway antenna system is engineered for quick assembly and straightforward operation. Its modular structure allows the antenna to be disassembled into compact sections that can be safely packed into airline transportable cases. This design significantly simplifies logistics and reduces transportation costs, especially for international projects or emergency response missions. In typical field conditions, one operator can complete system assembly and satellite acquisition within a short time. The manual azimuth and elevation adjustment mechanisms provide precise alignment capability without relying on complex motorized tracking systems. This reduces system complexity and ensures dependable performance even in environments where power supply may be limited or unstable.  2. Stable and High-Performance Signal Capability Equipped with a precision-engineered 1.2-meter reflector, the antenna delivers reliable gain performance suitable for professional communication applications. The system can be configured for Ka-band, Ku-band, or X-band operation according to project requirements. The reflector surface accuracy and structural rigidity are carefully optimized to maintain consistent RF performance under various environmental conditions. The antenna structure is designed to withstand moderate wind loads during operation. Its mechanical stability ensures minimal signal degradation, even in challenging outdoor environments. This makes the system highly suitable for field broadcasting, temporary communication hubs, disaster recovery operations, military exercises, and remote engineering projects. 3. Simple Structure, Reduced Maintenance Unlike fully motorized or auto-tracking systems, the manual flyaway antenna adopts a mechanically robust design with fewer electronic components. This approach greatly reduces the risk of system failure and lowers long-term maintenance costs. The simplified structure also allows easier troubleshooting and faster on-site servicing if required. For customers operating in remote regions where technical support resources may be limited, reliability and maintainability are critical factors. The 1.2m manual flyaway antenna station addresses these concerns by combining mechanical durability with proven RF performance.  4. Flexible Configuration Options To meet diverse customer requirements, the system can be integrated with various BUCs, LNBs, and RF chains depending on transmission power and bandwidth needs. It can also be supplied as a complete turnkey package including feed system, cables, and optional accessories. Customization options are available to comply with specific regional or project standards. This flexibility allows customers to tailor the system for government projects, commercial communication networks, broadcast applications, or specialized mission-based deployments. 5. The Ideal Balance Between Mobility and Performance Compared to larger fixed earth stations, the 1.2m manual flyaway antenna offers significantly greater mobility while still maintaining strong signal performance. It is particularly suitable for users who require a transportable solution without compromising communication reliability. For organizations seeking a cost-effective, field-proven satellite communication system, the 1.2m Manual Flyaway Antenna Station represents a dependable and practical investment. Its combination of portability, structural robustness, and stable RF performance ensures continuous connectivity whenever and wherever it is needed. If you are looking for a flexible satellite communication solution tailored to your operational needs, this system is ready to support your next project.  More Infomations about antesky manual flyaway antennas: https://antesky.com/project/1-2meter-flyaway-antenna-vsat-antena-portable/ https://antesky.com/project/1-set-of-1-2m-x-band-automatic-flyaway-antenna-syste m-shipped-to-korea/ https://antesky.com/project/projects-of-2-sets-of-1-2m-manual-portable-flyaway-a ntennas/ |
|||
| 4 | VSAT technology and installation / Dish pointing and alignment / Tracking Accuracy of Satellite Antenna: Definition, Measurement, and Calculation on: Feb 26th, 2026 at 7:22am |
||
|
|
|||
In the previous chapter on Pointing Accuracy of Satellite Antenna: Definition, Measurement, and Calculation, we introduced the concept of antenna pointing accuracy. Today, we will discuss another important performance parameter for satellite communication antennas: tracking accuracy. What is Tracking Accuracy of Satellite Antenna? Tracking accuracy of an antenna refers to the ability of its servo control system to real-time and stably align with a target satellite during dynamic operations. In simpler terms: “Can the antenna ‘stick’ to the target when either the target or the antenna is moving?” Tracking accuracy is usually expressed as a statistical measure of angular deviation, such as RMS (root mean square) or maximum instantaneous deviation, and the unit is degrees (°). In What Scenarios Does Satellite Antenna Need to Track a Satellite? There are often questions like: Question 1: Only mobile antennas need tracking accuracy, right? Fixed antennas pointing to GEO satellites don’t need it? Question 2: If either the satellite (or target) or the antenna is moving, then the antenna needs tracking and thus has a tracking accuracy specification, right? In fact, whether an antenna needs to track a satellite does not depend on whether the antenna is “moving” or “stationary”; it depends on the relationship between the antenna’s beamwidth (HPBW) and the relative angular motion of the target. Engineering guideline: If the target’s motion causes the antenna pointing to deviate by more than 10%–20% of the beamwidth, an automatic tracking system must be used, and tracking accuracy becomes a critical performance parameter. For example, the beamwidth of a parabolic antenna can be approximately calculated as: θ ≈ 70 * λ / D Where: θ = beamwidth (degrees) λ = operating wavelength (meters) D = antenna aperture (meters) Based on this principle, we can consider several typical scenarios: Scenario 1: Satellite Antenna is stationary, satellite is moving This mainly applies to LEO (Low Earth Orbit) and MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) satellites. These satellites move rapidly relative to the ground, with pass durations ranging from a few minutes to tens of minutes. Ground antennas must track the satellite smoothly, quickly, and accurately. Any lag or jitter in tracking can cause a sharp drop in signal quality or even communication loss. Tracking accuracy determines whether the communication link can remain stable during satellite passes. Scenario 2: Large fixed ground satellite antenna tracking GEO satellites For GEO satellites, the situation is more nuanced. GEO satellites are not perfectly stationary relative to Earth; their orbits experience small perturbations, usually within ±0.1°. From a ground observer’s perspective, the satellite traces a tiny figure-eight in the sky over 24 hours. Small-aperture ground antennas (e.g., 1.2 m at Ku-band, λ = 0.025 m) have a beamwidth: θ≈70 * 0.025 / 1.2≈1.5° The GEO satellite drift (±0.1°) is much smaller than the beamwidth, so signal degradation is minimal. Typical operation: Initial programmatic tracking aligns the antenna to the satellite. Servo stops; only reactivated when switching satellites. Large-aperture ground antennas (e.g., 10 m at Ku-band) have a beamwidth: θ ≈ 70 * 0.025 / 10 ≈ 0.175° Here, satellite drift (±0.1°) is comparable to the beamwidth, which can cause significant gain loss. Thus, automatic tracking (e.g., monopulse tracking) is required. The ACU periodically or based on signal quality (e.g., AGC voltage drop) triggers tracking adjustments. This runs continuously to compensate for slow satellite drift.  Authority Standards: Intelsat IESS-207 (Ku-band): Antennas ≥ 3.5 m must have automatic tracking. Intelsat IESS-308 (C-band): C-band Standard A antennas ≥ 7 m must have automatic tracking. Intelsat IESS-601 (Ka-band): Antennas ≥ 1.2 m are recommended or required to have automatic tracking; for large gateway stations (>3.5 m), it is mandatory. Scenario 3: Target is stationary, satellite antenna is moving (Satcom On-The-Move, SOTM) This is the typical SOTM scenario, where antennas mounted on moving platforms track GEO satellites. The servo system must not only point accurately but also compensate for platform motion (pitch, roll, sway) in real-time. Scenario 4: Both satellite antenna and target are moving Here, the antenna is on a moving platform tracking LEO or MEO satellites. Sources of Tracking Error Tracking errors mainly come from: External environment Servo system itself Signal carrier-to-noise ratio (C/N) Satellite ephemeris errors 1. External environment errors: Wind: wind pressure creates torque on the antenna structure. If servo torque is insufficient, continuous pointing error occurs, especially with gusts. Atmospheric effects: refraction shifts the apparent satellite position, particularly at low elevation angles, causing tracking error. 2. Servo system errors: Mechanical errors: Motor and gearbox backlash: creates response delay and dead zones, especially at low speed or frequent reverse corrections. Structural deformation: thermal expansion, wind loading can deform reflector, back structure, or feed support arm, altering phase center and pointing. Antenna pedestal misalignment: non-orthogonality of azimuth/elevation axes, bearing runout, etc. Control loop errors: Servo bandwidth limit: system cannot respond to fast disturbances (gusts) or rapid LEO passes, causing lag. Algorithm errors: different tracking algorithms introduce different error types. Sensor errors: Angular encoder: resolution, eccentricity, quantization errors convert directly into pointing error. IMU (gyros, accelerometers): bias drift, scale factor errors, noise cause attitude reference errors. 3. Signal carrier-to-noise ratio: High C/N is essential; low C/N increases tracking error, reduces stability, or may cause complete signal loss. 4. Satellite ephemeris errors: In programmatic tracking of LEO/MEO satellites, tracking is based on predicted satellite position from downloaded ephemeris. Any prediction error accumulates over time, directly contributing to tracking error. Measurement and Calculation of Tracking Accuracy On-site testing system consists of tracking system, controlled antenna system and spectrum analyzer, as shown in Figure. Test Steps When testing the step tracking accuracy, you should select a Satellite with small drift and stable beacon as the aim Satellite. Make the antenna point to the aim Satellite (Observe by the spectrum analyzer and make the tracking signal maximum), read and record the antenna Az position Pa0and El position Pe0at this time. Set up the tracking signal loop;record the tracking signal frequency F0. Adjust the gain of the tracking loop to make the tracking level as about 6V, and also set this signal level as the maximum level. Control antenna Az and El to deviate from the Satellite appropriately, then start step tracking. When the step tracking becomes in waiting state, read and record antenna Az position Paiand El position Pei, So Az tracking error at this time (Considering the secant compensation) Dai=|(Pai-Pa0)cosPe0|, El tracking error at this time Dei=|Pei-Pe0|. n(n³10)times repeat the Step 3, Az and El should be deviated to different direction, and get a group of tracking error data, so the tracking accuracy is |
|||
| 5 | Service Providers / Satellite Connection in Africa / Re: Introduction of Inclined Orbit Satellite Services on: Feb 25th, 2026 at 2:56pm |
||
|
|
|||
From forum admin: Aal the images that were embedded in the above messages were stored on freeimagehosting.net Unfortunately all the images have disappeared. Eric |
|||
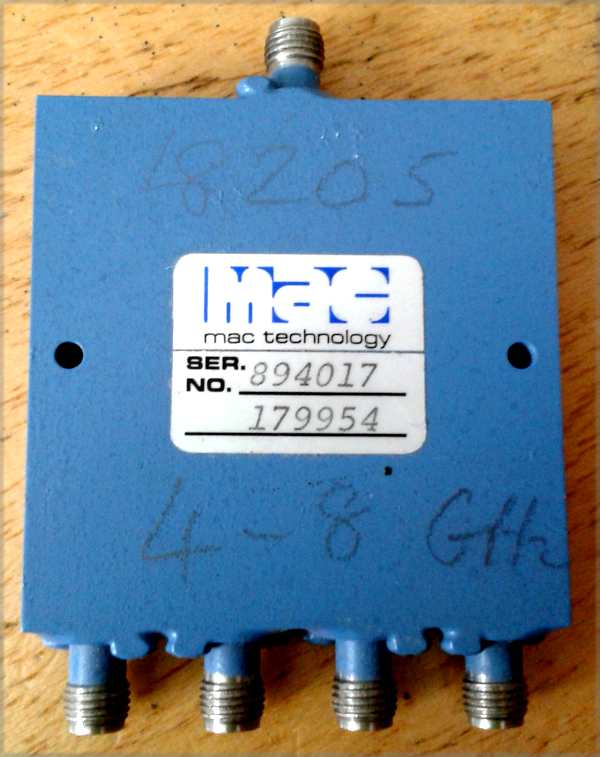
| 6 | VSAT technology and installation / Hub and VSAT satellite equipment for sale and wanted / For sale: MAC Technology 4-Way Power Divider, 4-8 GHz SMA connectors on: Feb 22nd, 2026 at 3:44pm |
||
|
|
|||
| 7 | Anything else / General and other topics / Re: Satellite communications and Artificial Intelligence on: Feb 21st, 2026 at 12:55pm |
||
|
|
|||
These are the top three pages reported by Bing "AI Performance. Citation sources: Microsoft Copilots and Partners" 1. Shows aerial photos of property address 2. About low noise block (LNB) converter 3. List showing how many geostationary satellites are there in orbit The top one (1) simply uses Google Maps API to give you an aerial view of your house, with an option for terrain height information. If you want satellite dish pointing data for your area you are better going to my maps index page https://www.satsig.net/maps/ and picking a page that covers your general country or location. The two other pages (2) and (3) are satellite communications related. If you find any errors in these pages, please tell me. |
|||
| 8 | Anything else / General and other topics / Re: Satellite communications and Artificial Intelligence on: Feb 19th, 2026 at 6:37pm |
||
|
|
|||
Just a reminder... According a report from Microsoft Bing, during the past three months, 137 pages from this web site have been cited in AI outputs. Total number of occasions = 9527 This report gives me mixed feelings. First, I am delighted that AI finds the site's content of interest. Second, it make me realise how important it is that the site content is factually correct. All the regular content .htm type web pages are my creation and are not AI generated. I can't say for certain however regarding content in these forum pages. Of the total of 136 pages, 18 are from this forum and I will be slowly going through them, editing to improve clarity, check that any links work and that links go to useful places. Since you, as a visitor, may have knowledge of satellite communications please provide me with feedback if you find any errors. Please say the page url and explain what is wrong and provide your suggested correction. Email me at eric@satsig.net Best regards, Eric. |
|||
| 9 | Anything else / General and other topics / Re: Understanding Antenna Standing Wave Ratio (SWR) on: Feb 8th, 2026 at 8:31pm |
||
|
|
|||
The above posting about VSWR reminds me of an experience I had connecting high power amplifiers with rectangular waveguide output to an antenna which had rectangular waveguide inputs. For the cross site connection, I was supplied with a very long length of Andrew HELIAX ellipti-guide which was elliptical corrugated copper tube waveguide with a black outer sheath. I was also given two rectangular to elliptical waveguide adaptors to go at either end.  Illustrated: Ellipti-guide adaptor. These waveguide adaptors each had 3 small tuning screws intended to improve the VSWR across the elliptical to rectangular transitions. The image above shows a pressure dry air connector. The 3 tuning screws are underneath. I wondered how to make these adjustments. Starting at the HPA, I installed a high loss (-40 dB) cross waveguide coupler at the end of the rectangular guide with the coupling direction facing backwards to the intended power flow.  Illustrated: Two Ku band cross-waveguide couplers. So, when power was going from the HPA (rect) to the ellipti-guide any power coming out the side arm would relate to the reflected component from the antenna and backwards towards the HPA. This worked well and I was able to take measurements across the intended 14-14.5 GHz frequency range and adjust the screws for minimum reflections. While this was going on, the antenna end of the long cross site ellipti-guide was terminated in a dummy load. The process was then repeated at the waveguide transition at antenna end with the antenna connected, with emphases on very low power and the dish pointed safely away from the geo orbit. Measurements were done with sensitive spectrum analyser. If you try anything like this take care. The microwave HPA output is hazardous. Hazard to yourself (mainly your eyes) Hazard to the satellite (interference) Hazard to your test equipment (burning out expensive spec an or sensors) If you are connecting a spectrum analyser or power meter to the side arm of the cross-waveguide coupler do the calculations first and check that the levels into the meter will be acceptable. e.g. 400W forward power, 40 dB cross waveguide power monitor point in the forward direction. 400W = 26 dBW = 56 dBm Coupler loss = -40 dB So power to spec an or power sensor head = 56 - 40 = +16 dBm. See also here for microwave power measurement |
|||
| 10 | Anything else / General and other topics / Understanding Antenna Standing Wave Ratio (SWR) on: Feb 6th, 2026 at 3:17am |
||
|
|
|||
What is SWR? The Standing Wave Ratio (SWR) is a measure of how well an antenna is matched to the transmission line and the transmitter. When an RF signal travels along a transmission line and encounters a mismatch, some of the energy is reflected back, creating a standing wave. At points where the incident and reflected waves are in phase, their voltages add to form a maximum voltage, called the voltage antinode (Vmax). Where they are out of phase, the voltages subtract, forming a voltage node (Vmin). Other points along the line have voltages between these extremes. This resulting wave pattern is called a standing wave, and the SWR is defined as the ratio of the voltage at an antinode to that at a node: SWR=Vmin/Vmax In RF measurements, the SWR measured using a slotted line or other methods can be used to calculate the reflection coefficient and absorption coefficient of materials. 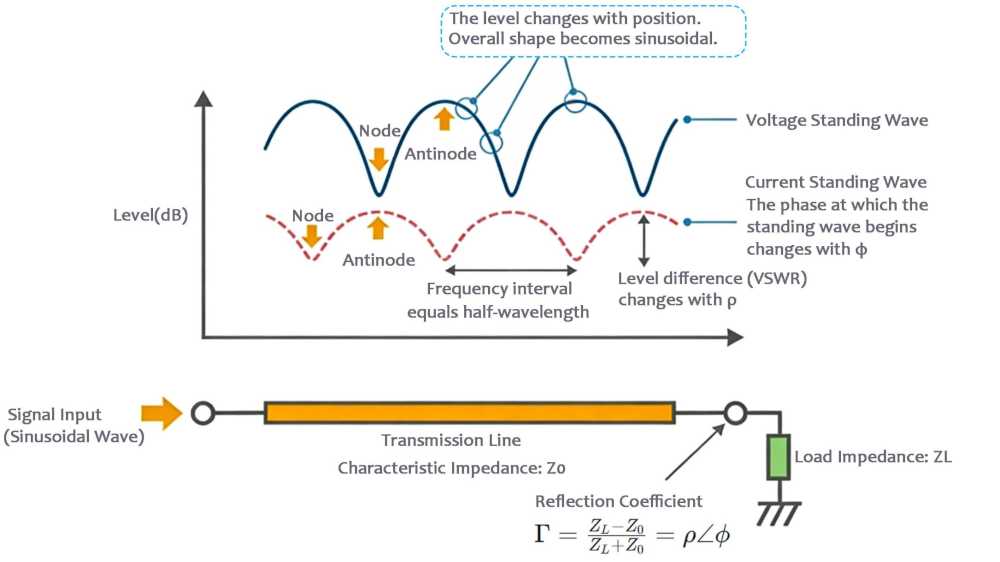 Why SWR Matters For RF systems, impedance matching is crucial. A low SWR ensures that most of the transmitted power is radiated by the antenna rather than reflected back to the transmitter. In broadband systems, SWR can vary across frequency, so the goal is to achieve good impedance matching across the entire operating range. Ideal SWR: SWR = 1 means perfect matching; all transmitted power is radiated, with no reflection. SWR > 1: Indicates some power is reflected back, potentially heating the feedline and, at high levels, damaging the transmitter. Common SWR Requirements and Measurement Typical targets: Mobile communications often require SWR < 1.5, while many applications aim for SWR < 2.0. Measurement tools: SWR meters, vector network analyzers (VNAs), or antenna analyzers are commonly used. Adjustment methods: Antenna tuning or matching networks can improve impedance matching and reduce SWR.  Why Do Standing Waves Form? Ideal case: If the transmitter output impedance, transmission line characteristic impedance, and antenna input impedance are all equal (typically 50Ω or 75Ω), all energy flows to the antenna with no reflection. Only a forward traveling waveexists on the feedline. Practical case: Antenna impedance varies with frequency, environment, and installation, making perfect matching difficult. Mismatch and reflection: When impedance is mismatched, part of the energy cannot be absorbed by the antenna and is reflected back toward the transmitter. Formation of standing waves: The reflected wave combines with the incident wave, creating points of maximum and minimum voltage along the line — the “standing wave.” SWR quantifies the severity of this mismatch and reflection. How to Calculate SWR SWR is often expressed as a ratio like 1.5:1 or 2:1 (usually we just say “SWR = 1.5”). Formula using reflection coefficient Γ: SWR=1+∣Γ∣/1−∣Γ∣ where ∣Γ∣ is the voltage reflection coefficient (ratio of reflected voltage to incident voltage), determined by how much the load impedance differs from the line impedance. Intuitive formula using impedances: SWR=Zload/Zline or Zline/Zload,take the larger value Example: If the feedline is 50Ω and the antenna is 100Ω, SWR = 100/50 = 2:1. If the antenna is 25Ω, SWR = 50/25 = 2:1. The further the impedance deviates from the line, the higher the SWR. How to Improve (Lower) SWR The key to improving SWR is improving impedance matching: Use a properly designed antenna: Ensure it operates well within the target frequency range. Use an antenna tuner: This device inserts a variable matching network between the transmitter and antenna, lowering the overall SWR on the feedline. Note: it does not change the antenna’s inherent SWR but protects the transmitter. Adjust antenna dimensions: For single-frequency antennas (like dipoles), fine-tune the element length to achieve resonance at the desired frequency, minimizing SWR. Ensure solid connections: Check connectors for tightness, oxidation, or moisture. Consider the installation environment: Keep antennas away from metal objects and walls and ensure sufficient height, as surroundings can significantly affect impedance. Summary SWR is a key “health indicator” of an antenna system, showing how efficiently energy is transmitted from the transmitter to the antenna. Low SWR means high energy transfer efficiency and a safe, stable system. Measuring and monitoring SWR is fundamental for any RF system, especially for transmitters. |
|||
Email me: eric@satsig.net
Powered by YaBB 2.5.2!
YaBB Forum Software © 2000-. All Rights Reserved.
Disclaimer, Terms of Use and Privacy Forum User Agreement Forum rules Cookie policy.