|
|
R-BGAN - Regional Broadband Global Area Network
R-BGAN network system:
To provide satellite internet access direct to laptop sized portable terminals.
See
http://www.everest.co.jp/sat/sat_main.htm for example pictures.
How does R-BGAN work:
The solution is to have high power transmission in the downlink and high sensitivity satellite uplink sensitivity. This is largely achieved simply by using a large 10m diameter antenna on the satellite. The earliest satellites (e.g. Telstar) used low power, say 1 watt, into its antennas with gain of 3 dBi or so plus 30m diameter dishes on the ground. The R-BGAN idea simply reverses this arrangement so there is nothing too improbable about it.
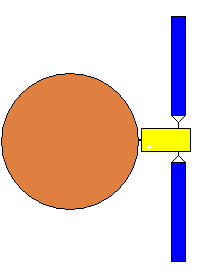
My idea of what the satellite looks like.
The feed array will need to generate some 100 spot beams, each approx 1.8 deg beam-width, thus covering all the visible surface of the earth, which looks like a circle approx 18 degrees diameter as seen from the R-BGAN satellite. With such a design it is possible to have an uplink G/T per beam of 17 dBK (10m dia, 1.6 GHz, 300K)
On the downlink, beam gain will be about 42 dBi giving a beam edge eirp of some 55 dBW when the power allocated to a beam is 40W. The power per beam will need to vary according to the traffic required. If you do the R-BGAN link budgets using https://www.satsig.net/linkbugt.htm you will find that uplink bit rates of 100 kbit/s and downlink bit rates of 144 kbit/s look quite feasible.
This is not 'broadband' as I understand the term in respect of cable modems, ADSL phone lines and fixed large satellite dish users, rather medium speed. Even the 144 kbit/s is shared amongst multiple users.
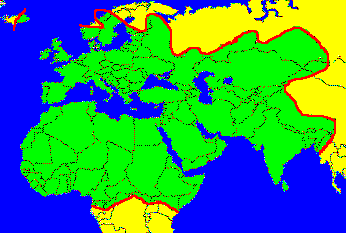
Coverage: My map above
Located at orbit longitude 65 degrees east the Thuraya R-BGAN satellite has coverage of Africa north of the equator, Europe, and Asia to the west of Calcutta.
Alternative, if you are happy with a static installation: Broadband Internet access in the Middle East using fixed 2-way dish, typically 1.2m diameter.
Example of how R-BGAN communications terminals may be of help in emergency situations:
Press release 12 Oct 2005 from Télécoms Sans Frontières (TSF)
They have rushed teams and equipment to help relief efforts in earthquake-hit Pakistan, where thousands are dead and millions of people remain homeless.
TSF is using a range of Inmarsat equipment to help rescue workers, including R-BGAN, GAN and Mini-M.
One team is at Muzaffarabad in Kashmir - the worst-hit region in northern Pakistan near the border with India - where it has established internet links at the heart of the United Nations' rescue centre. A second team has installed a telecommunications centre for the rescue workers based at nearby Mansehra.
Inmarsat-sponsored TSF responded immediately to the disaster on October 8, despatching a team from its base at Colombo in Sri Lanka within hours of the quake, which registered 7.6 on the Richter scale. Entire villages in northern Pakistan have been razed to the ground and roads blocked, creating conditions that severely hamper relief efforts. Four days after the quake, an estimated 2 million people were still without shelter in the affected areas, but as telephone links had been cut it was difficult for rescue teams to establish exact numbers. When responding to disasters, TSF's objective is swiftly to create emergency mobile satellite telecoms centres - using Inmarsat equipment - for rescue teams, local authorities and other emergency relief efforts.
The charity supplies telephone and fax lines, as well as technical assistance for computers and telecommunications, and helps to co-ordinate the exchange of information between rescuers.
|
Page started 12 October 2004, amended 27 Oct 2022. |